Stack and Queue
Stack (LAST IN FIRST OUT)
- Unlike an array, a stack does not offer constant-time access to the nth item. However, it does allow constant time adds and removes, as it doesn't require shifting elements around.
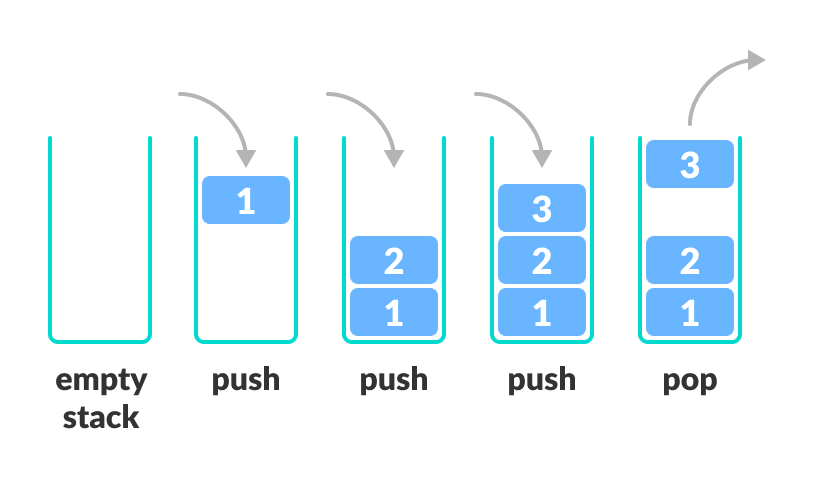
#regular list can be used as stack
stack = []
stack.append(12)
stack.append(45)
print(stack[-1]) #45 last in first out
Queue (FIRST IN FIRST OUT)
- A queue can also be implemented with a linked list. In fact, they are essentially the same thing, as long as items are added and removed from opposite sides.
- Enqueue = Add, Dequeue(POP)

from collections import deque
d = deque()
d.append(12)
d.append(13)
print(d.popleft()) #12 first in first out
Priority Queue
- The priority queue is an advanced type of the Queue data structure. Instead of dequeuing the oldest element, a priority queue sorts and dequeues elements based on their priorities.
- Priority queues are used to handle scheduling problems where some tasks are prioritized over others.
# the item with the lowest value is removed first
from queue import PriorityQueue
q = PriorityQueue()
q.put(4)
q.put(2)
q.put(5)
q.put(1)
q.put(3)
while not q.empty():
next_item = q.get()
print(next_item)
# we can add items alogside the priorite numbers
from queue import PriorityQueue
q = PriorityQueue()
q.put([4, 'Read'])
q.put([2, 'Play'])
q.put([5, 'Write'])
q.put([1, 'Code'])
q.put([3, 'Study'])
q.put([4, 's'])
while not q.empty():
next_item = q.get()
print(next_item)
# we can multiply with negative to get the defualt out put in reverse
from queue import PriorityQueue
q = PriorityQueue()
q.put((-4, 'Read'))
q.put((-2, 'Play'))
q.put((-5, 'Write'))
q.put((-1, 'Code'))
q.put((-3, 'Study'))
while not q.empty():
next_item = q.get()
print(next_item)
Priority Queue 2 (Heapq)
- Using heapq
heapify- This function is used to convert the iterable into a heap data structure.
heappush- This function is used to insert the element mentioned in its arguments into heap.
heappop- This function is used to remove and return the smallest element from heap.
Python's heapq is min heap implementation by default, but to get a max heap, you can multiply by -1 when inserting and multiply back by -1 when popping to get the max element.
import heapq
minHeap = []
# to add element
heapq.heappush(minHeap, 1)
heapq.heappush(minHeap, 13)
print(minHeap) #sorted array
print(minHeap[0]) #get the top max
# to remove elt
print(heapq.heappop(minHeap))
print(heapq.heappop(minHeap))
# if you already have an array populated with elts, use heapify
import heapq
minHeap = [4,5,6,7,8]
heapq.heapify(minHeap)
print(minHeap)